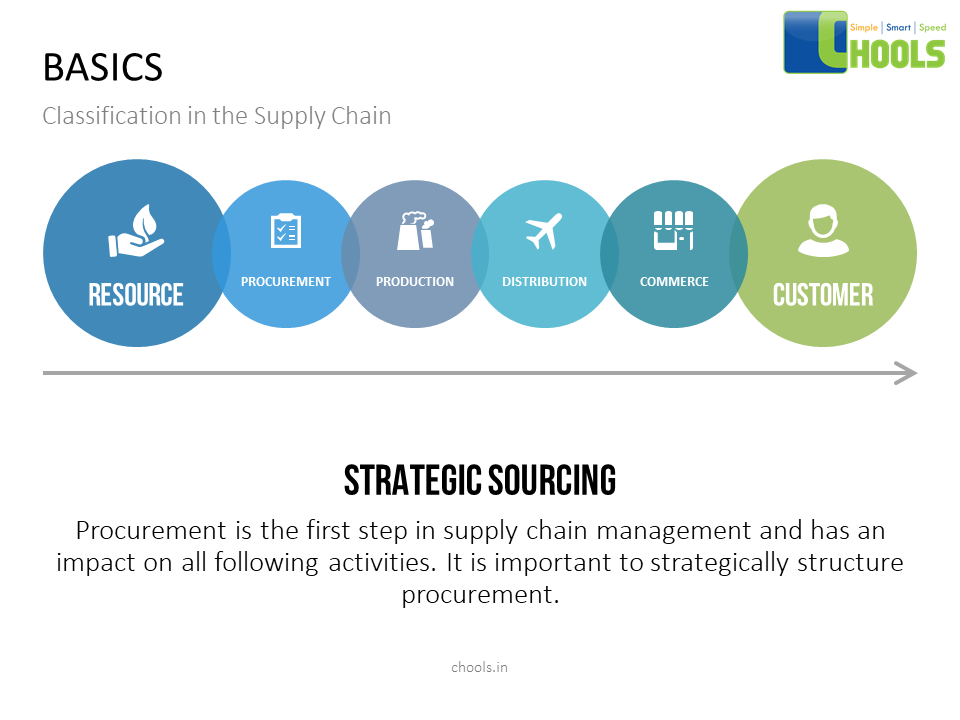
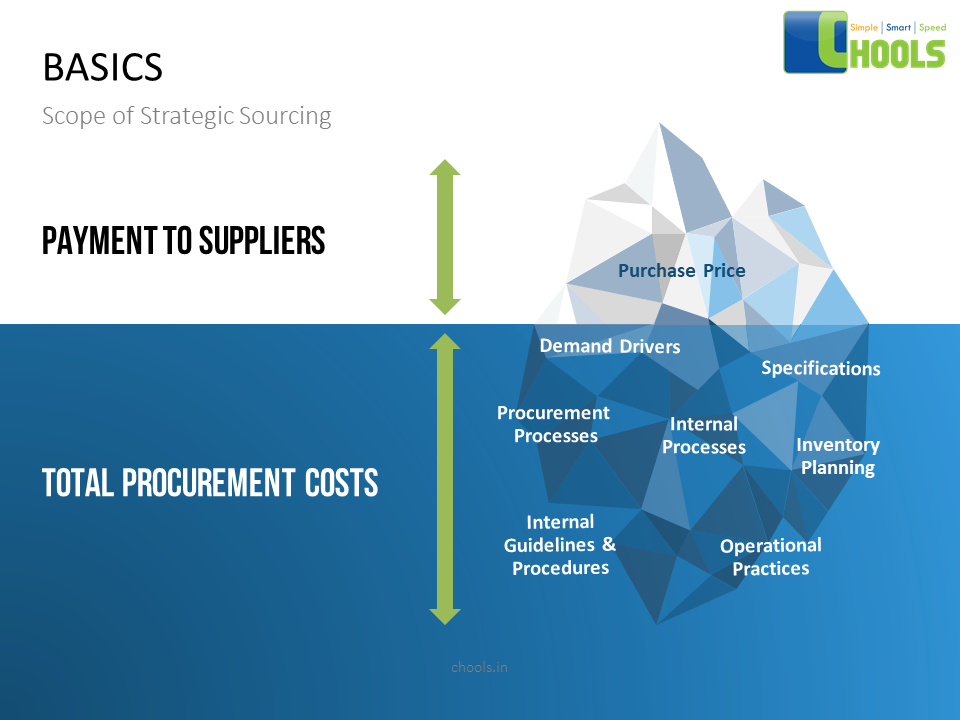
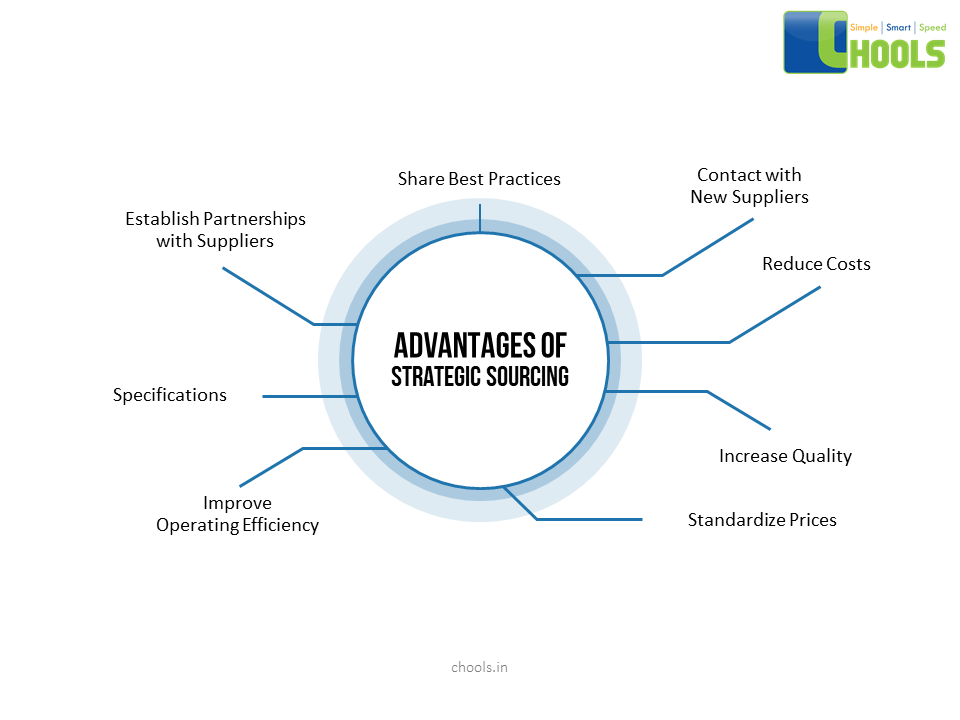
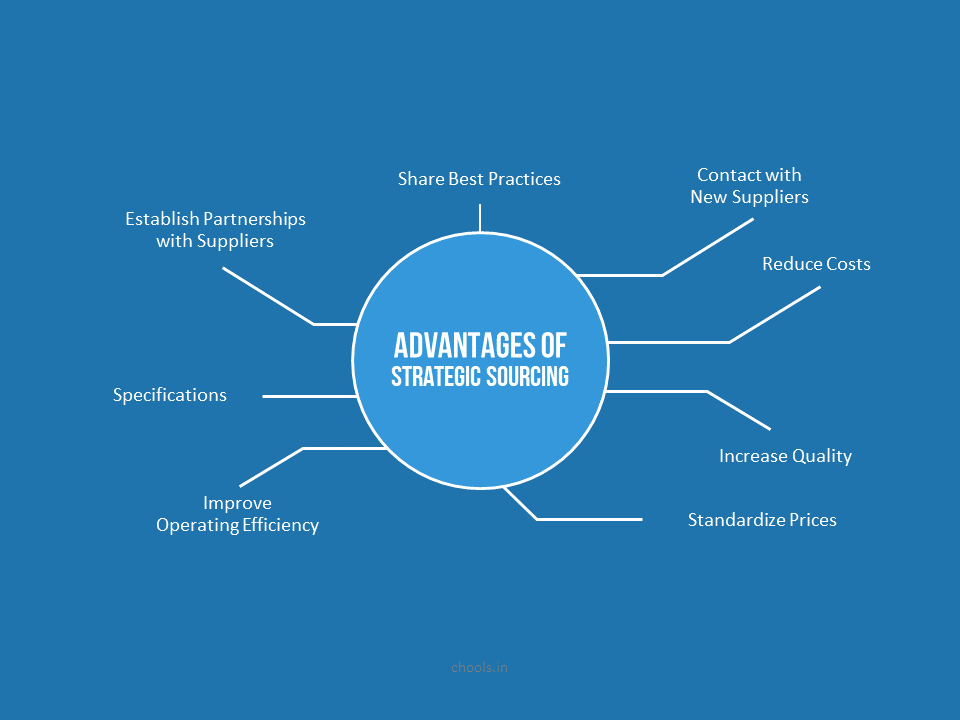
Sourcing and Network Collaboration
The industrial revolution has given way to the days of the digital revolution. If earlier it was about who had monopoly over the market, today it is about who knows how to outsource best. Outsourcing allows a company to focus on what it is good at, leveraging the capabilities of its partners to speed up production and distribution of its products. Unnecessary and cost-inefficient processes are swiftly cut off from the sum total of all that goes into the making of the product. Products moving from design to market is made faster by such collaboration.
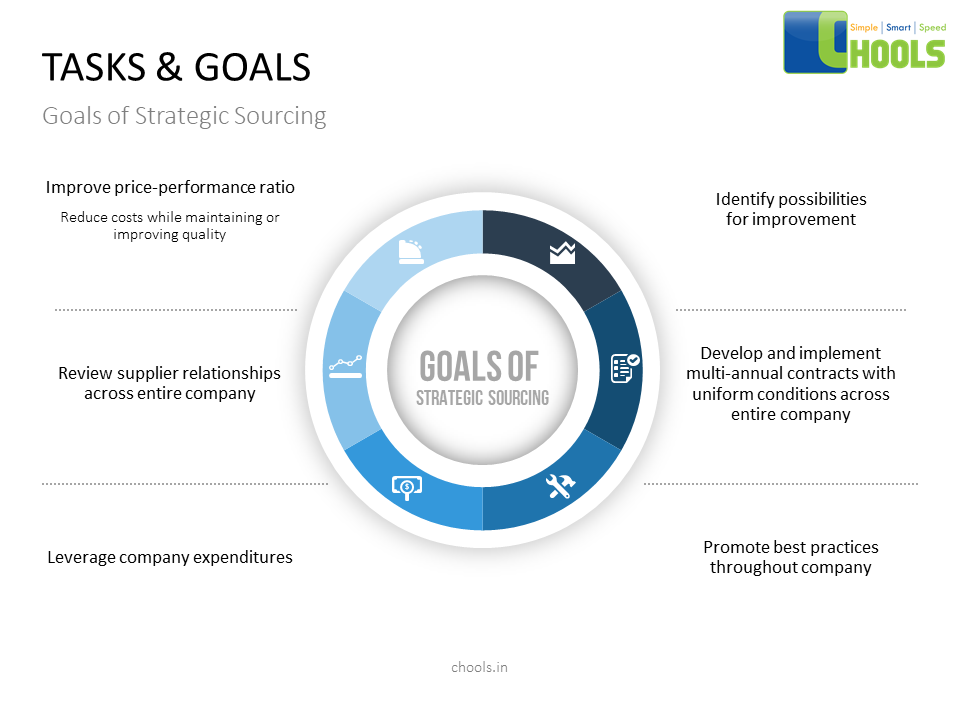
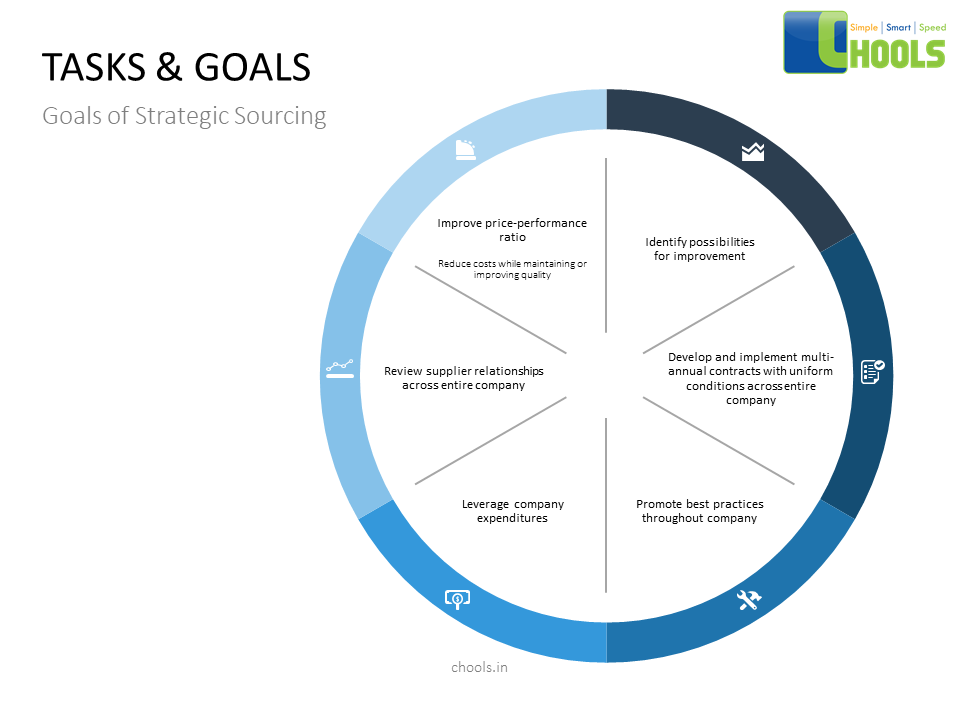
Why Sourcing and Network Collaboration is important –
Some reasons why industries have deconstructed their procurement strategies, and started collaborating to provide the end product is because –
✔ The Global Market is Volatile. Driven by fast changing trends, Economic Volatility is something every business needs to be prepared for.
✔ Most changes in Procurement are driven by a pressure to cut costs.
✔ A lack of necessary data for driving category strategies.
✔ Lack of category expertise in strategic spend areas.
✔ An increase in complexity in supply chains due to globalization.
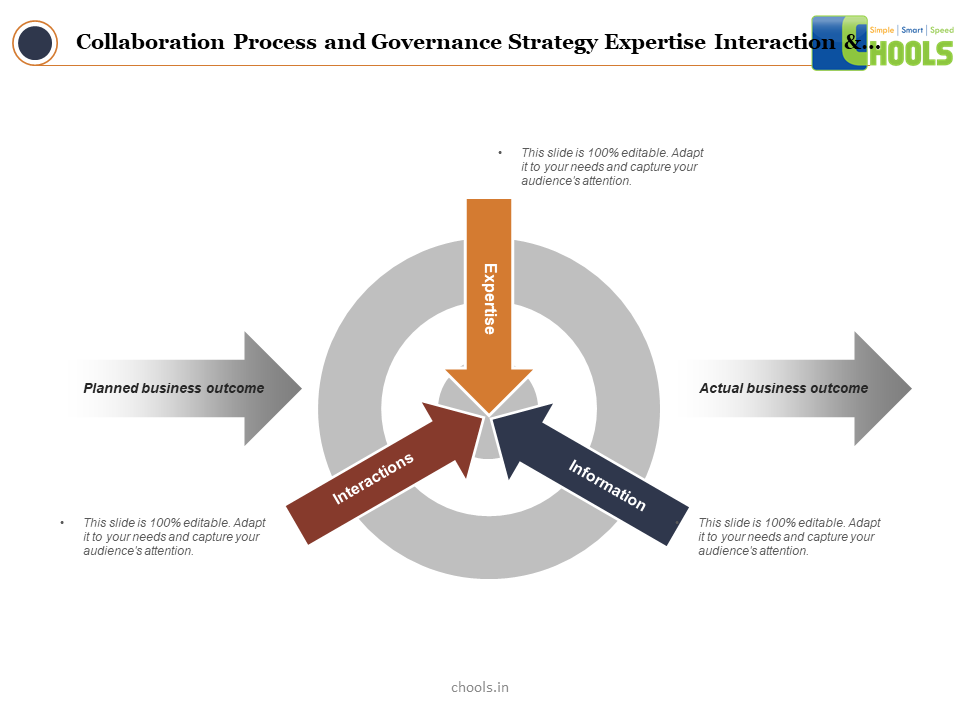
Supply Chain Sourcing and Network Collaboration depends on many-to-many architecture. Many-to-many refers to a process that enables many participants in a network to collaborate with many others.
Sourcing and Network Collaboration is a critical part of the supply chain. A part that allows for the digital transformation of the entire supply chain. Manually entered data is replaced with digital data. Information data gaps in the supply chain are removed, making for a more robust system. Sourcing and Network Collaboration involves planning, sourcing, making, delivering, managing returns, evaluating supply chain risks, and calculating supply chain finance.
Our Approach to Sourcing and Networking –
Studies have shown that a networked enterprise has a 50% chance of beating their peers by gaining higher sales and profit margins, placing themselves as a market leader. We help you do this is by –
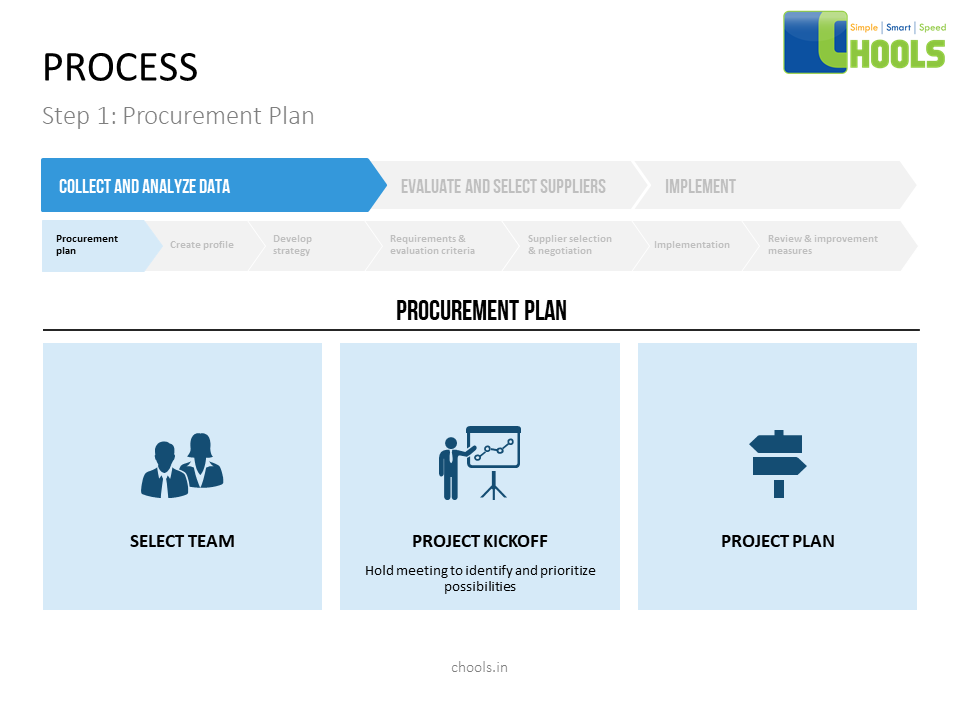
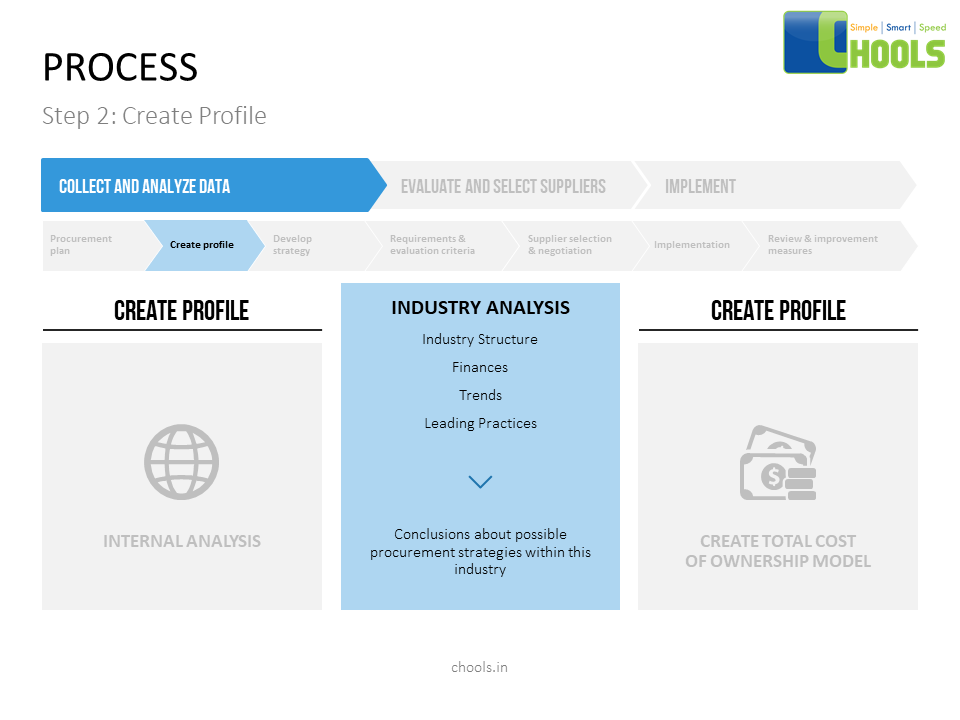
➤ Sourcing – Utilizing Discovery. Issuing RFx and collecting responses. Storing profile information. Creating category specific templates, and driving process adoption.
➤ Auction – Negotiating price. Maximizing competition. Increasing speed to savings by considering alternative spending and price scenarios.
➤ Critical aspects of Negotiation and Legality.
➤ Supplier quality standards and Relations.
➤ Risk management.
➤ Strategic analysis.
➤ Market forecasts.
➤ Competitive analysis.
We at Chools help you navigate through the complex path of Sourcing and Network Collaboration. Be ready for tomorrow, by joining hands with the best, and evolve in a drastically developing market.
Welcome to Chools.
Go Big! Grow Big!
Sourcing and Network Collaboration - Case Study
Problem –
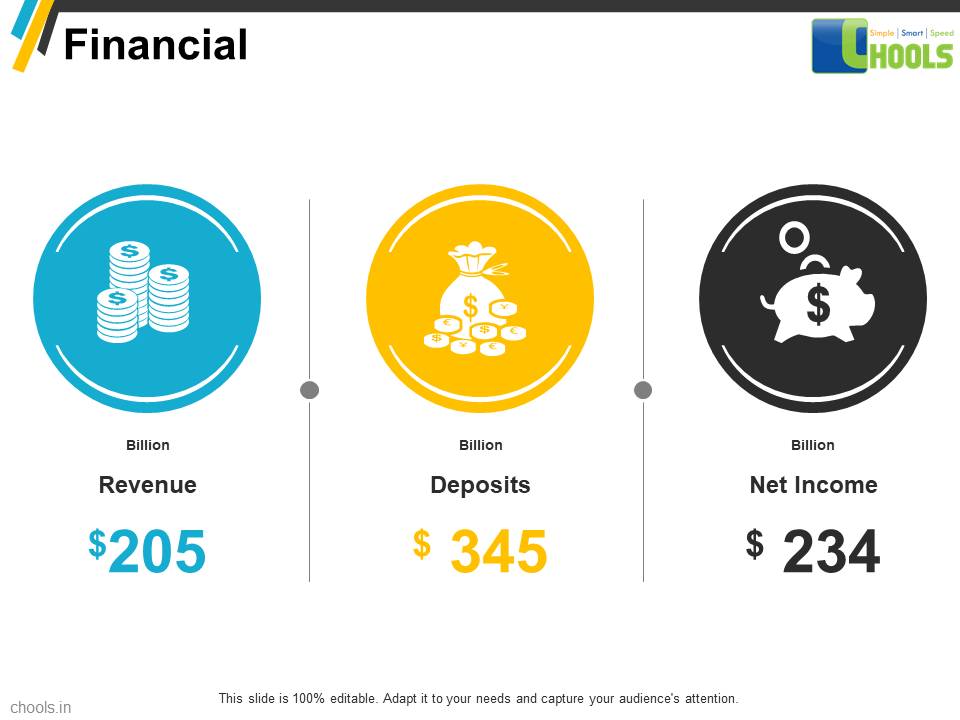
A world renowned company with multiple verticals, is known for their massive procurement volumes. Spread across the globe, the company has procured goods and supplies worth 20 billion euros, from a sum total of 112,000 suppliers, spread across 147 countries.
The massive levels of procurement also meant that adherence had to be maintained to the company’s ethical, environmental and social standards. When it came to the end product that was being produced, the company was not going for anything except the best. Considering the global scale of the business, this was no easy task.
A streamlining of processes was necessary to find out if the suppliers’ were meeting the company’s expectations.
Chools Consulting Services was consulted for this endeavor.
Solution –
Procurement staffs and suppliers needed to enhance their understanding of the process at hand. Procedural changes could be implemented across the company only once this was done. Sustainability standards within the supply chain were seen to be a strategic lever for the company to ensure competitiveness on a global level and identify the suppliers.
A sustainability development program was established, where the supply chain was assessed, to identify potential high risk suppliers. The base was set for the company’s sourcing and network collaboration strategies, based on this data.
Sustainability training programs for its employees dealing with procurement and suppliers followed. Sustainability audits were conducted on a regular basis. Several key collaborative initiatives were taken up for introducing higher standards to the suppliers.
Result –
What started off as a pilot initiative has now been integrated into the company’s main supply chain process. Chools was able to improve the company’s standards of data collection on both procurement and suppliers.
Problem –
An information tech giant has to cater to high sales volumes, and were finding trouble in doing so. In a time when the market was booming, their earlier tact was not working. Coming out with mass-produced products was not working out anymore, with cheaper replacements being available all over the market. The supply chain also needed a thorough refurnish. The journey of product to customer was facing several roadblocks. Each of which needed a new solution.
Solution –
The company was one of the first to understand the importance of sourcing and supply chain collaboration. Making the computer was no more about prototyping, designing and putting the product out in the market. They gave the consumers the option to customize the computers they ordered. This was a business model unheard of in the industry. The number of suppliers were reduced from 204 to 47. The locations of the company’s suppliers were also strategically placed, so that each of them were 15 minutes away from the main factory.
The production levels were now met in accordance to demand, decreasing inventory. The shippers housed the monitors for the computer systems, further decreasing inventory, lowering costs, and increasing efficiency.
Result –
➤ The time required for a computer to be ready for shipment was brought down by half.
➤ The new inventory system gave a 6% profit margin.
➤ The inventory turnover time increased by 57%.
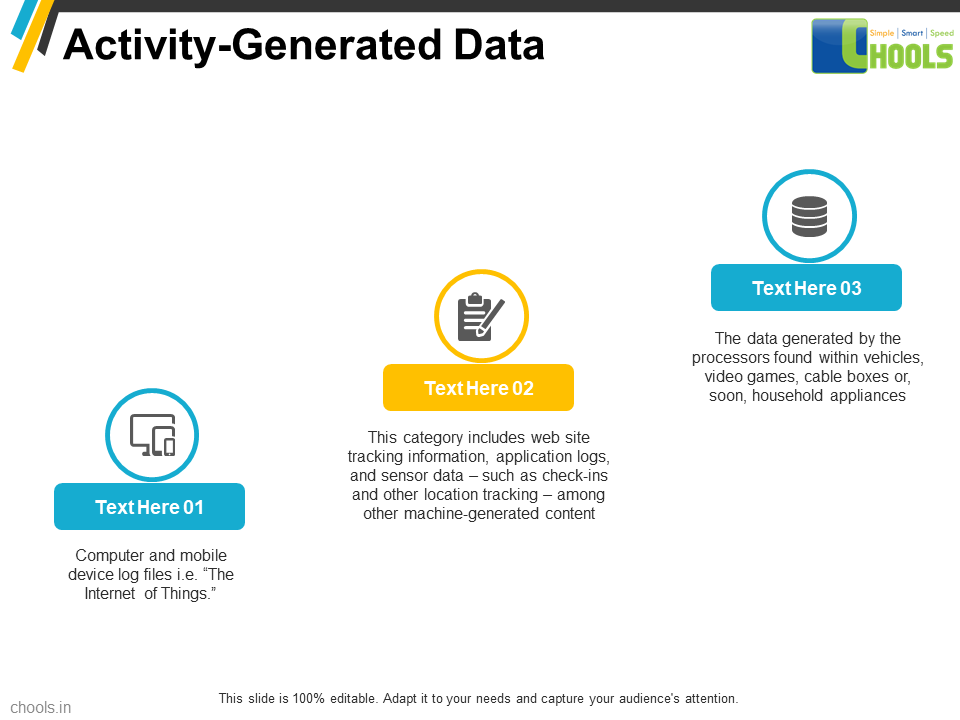
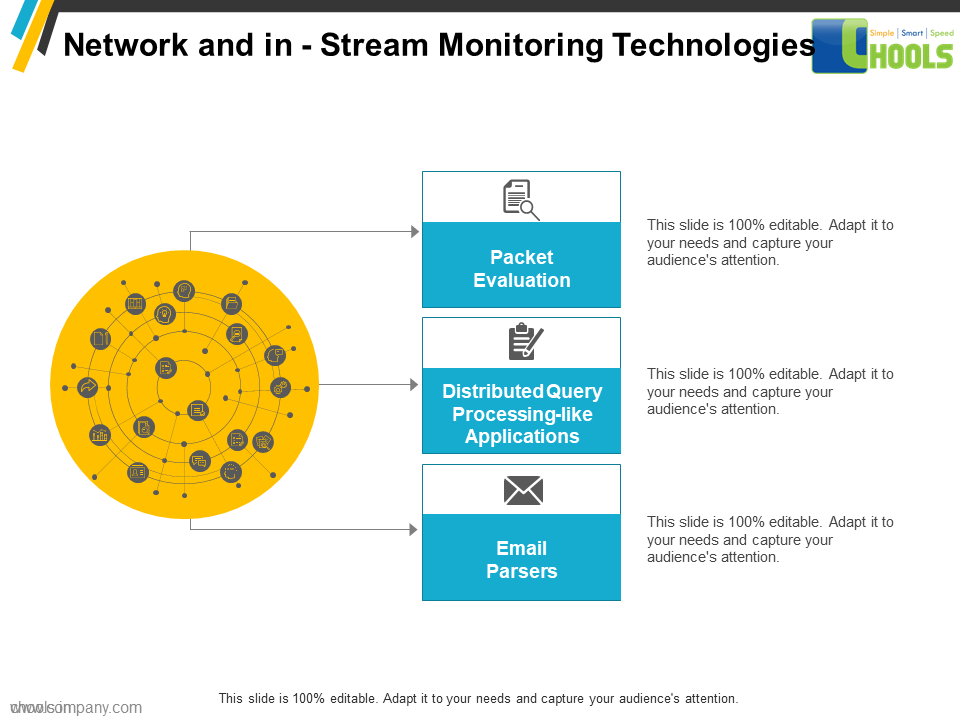
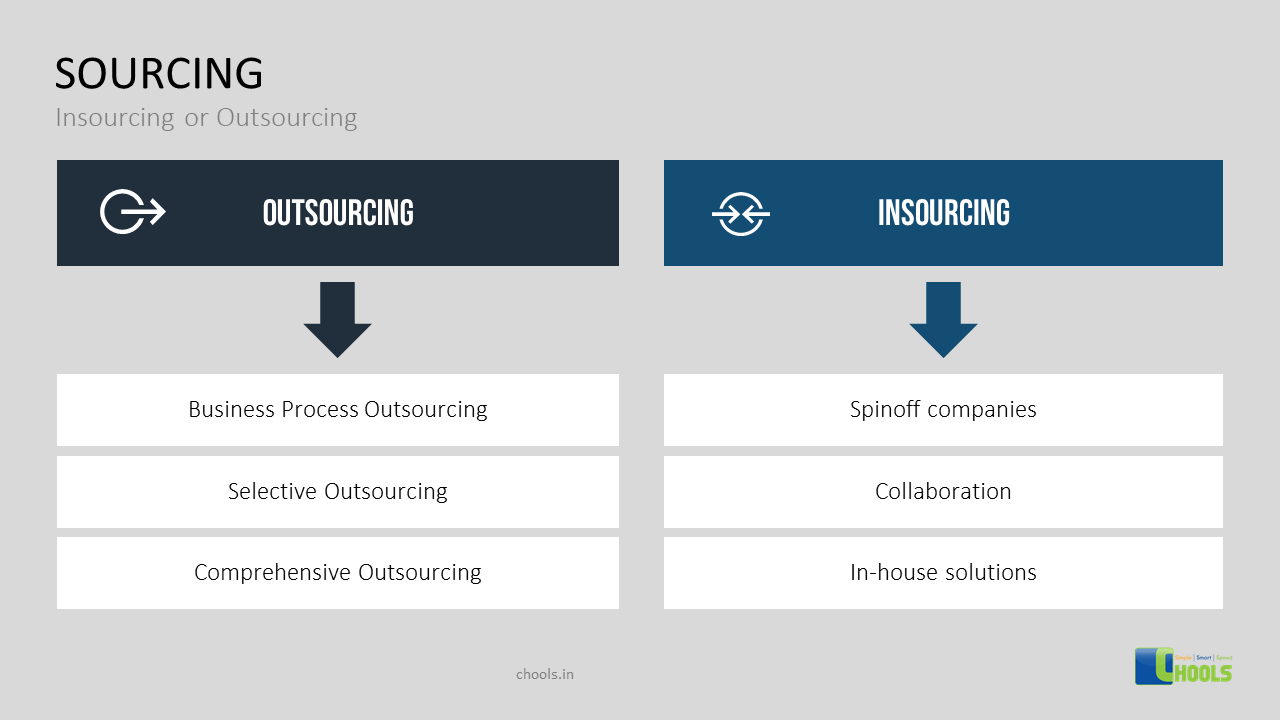
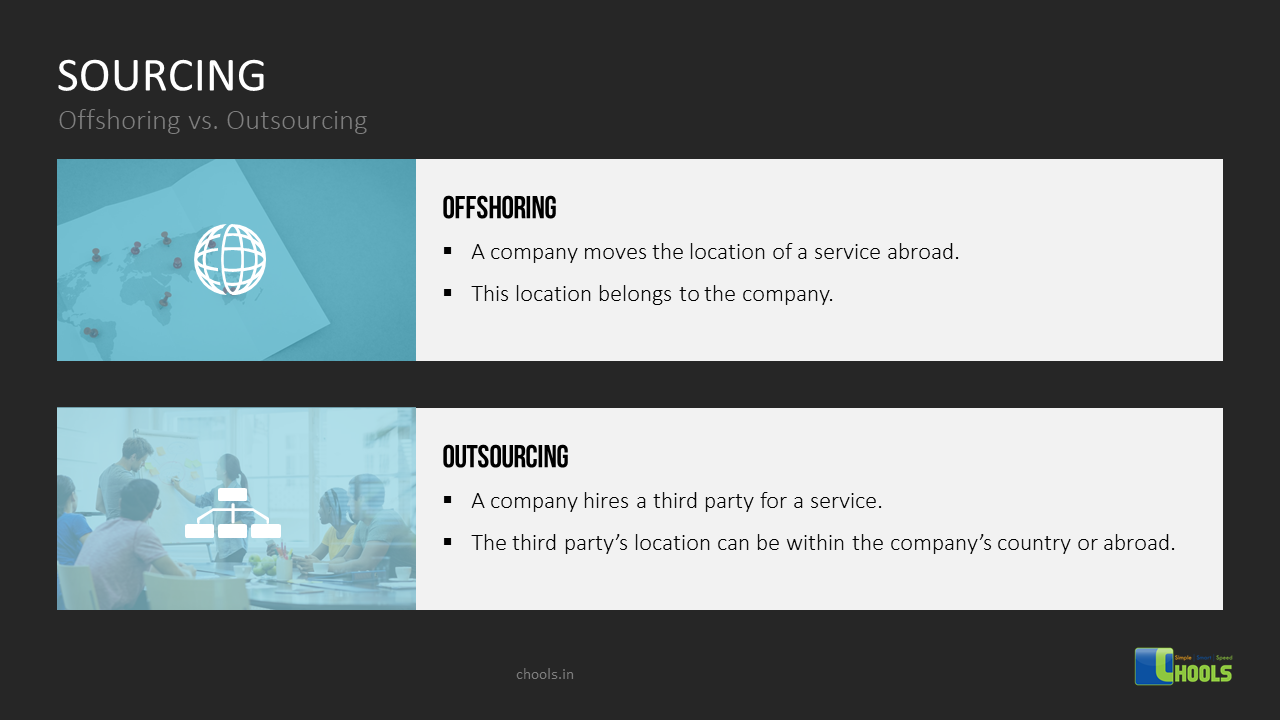
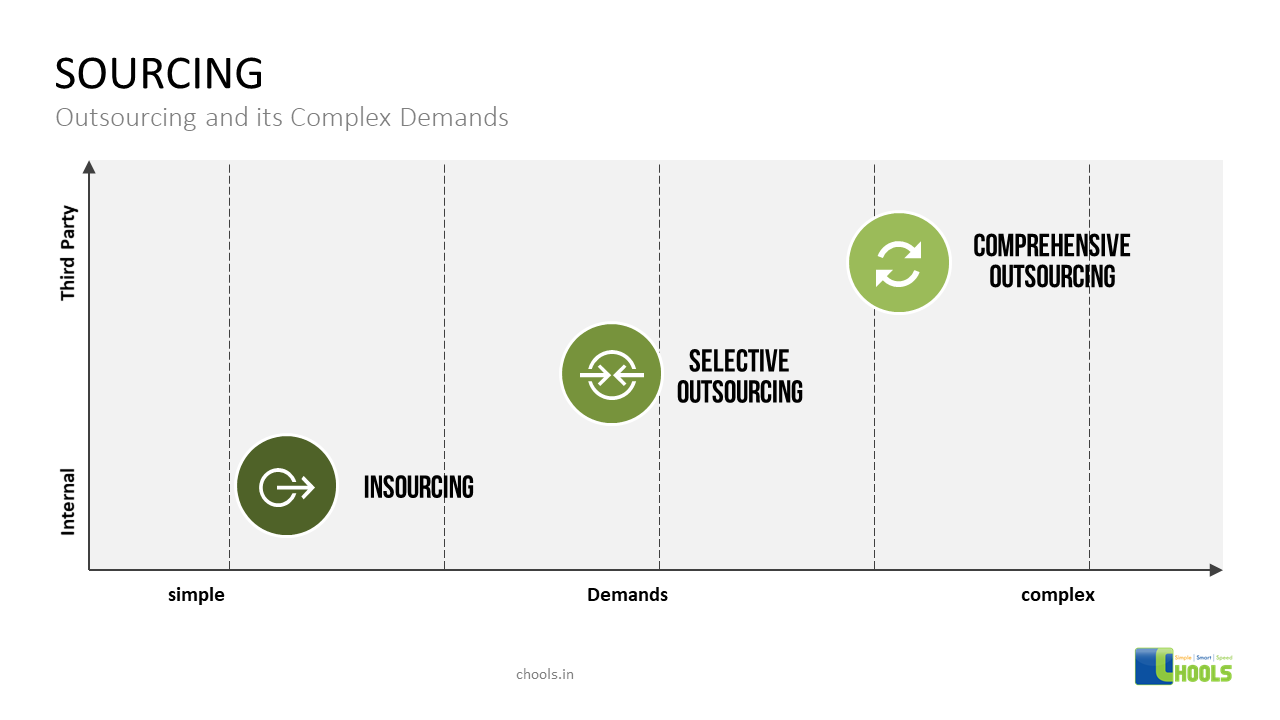
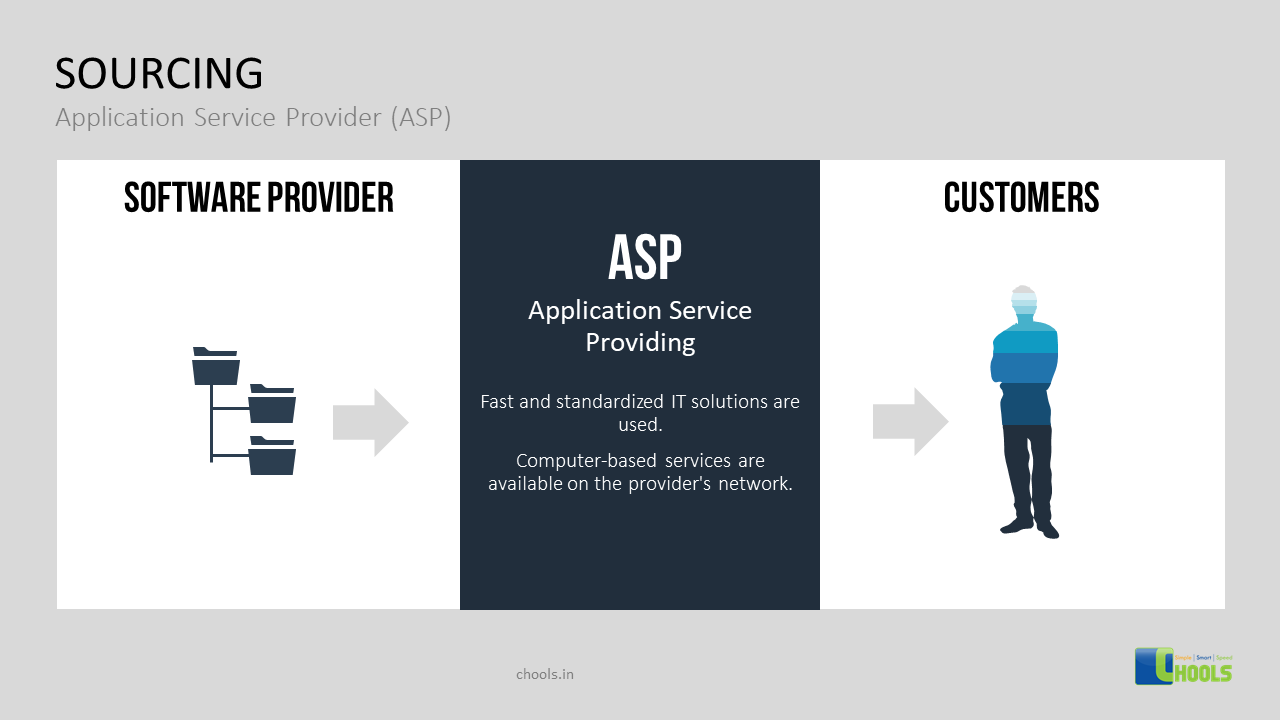
1. DATA-MINING SOURCES
2. COLLABORATION PROCESS
3. STRATEGIC SOURCING
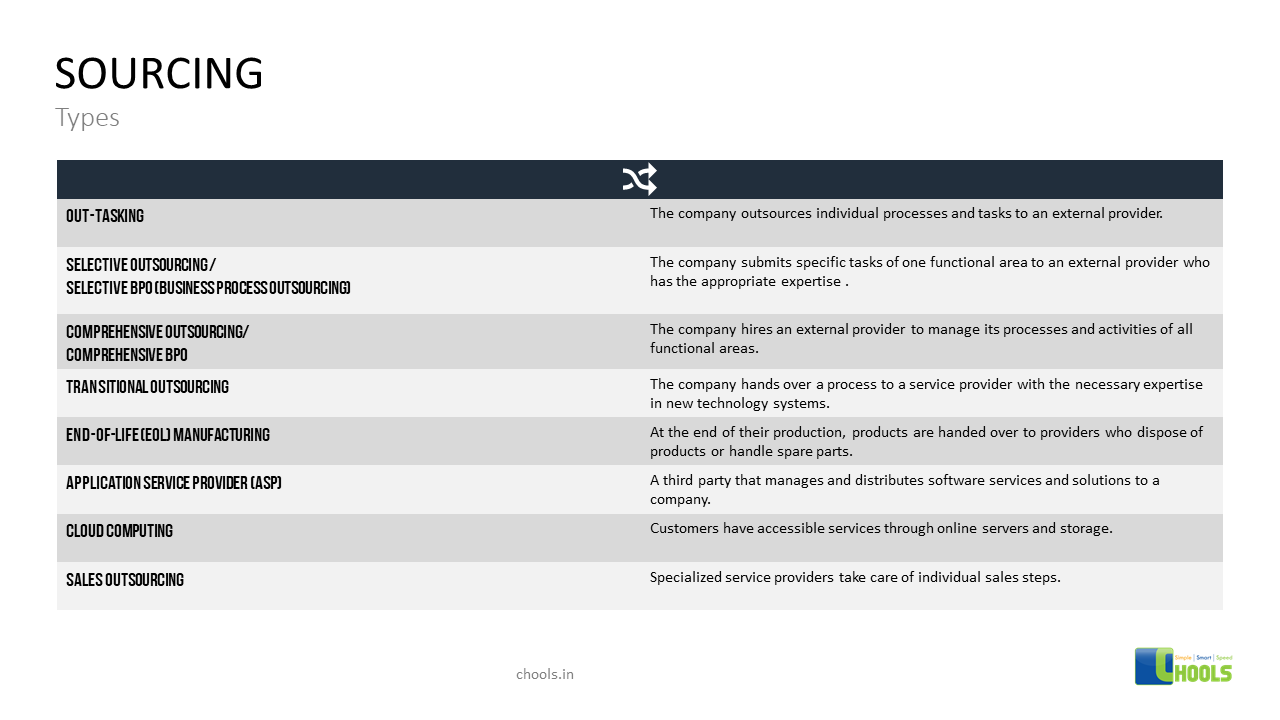
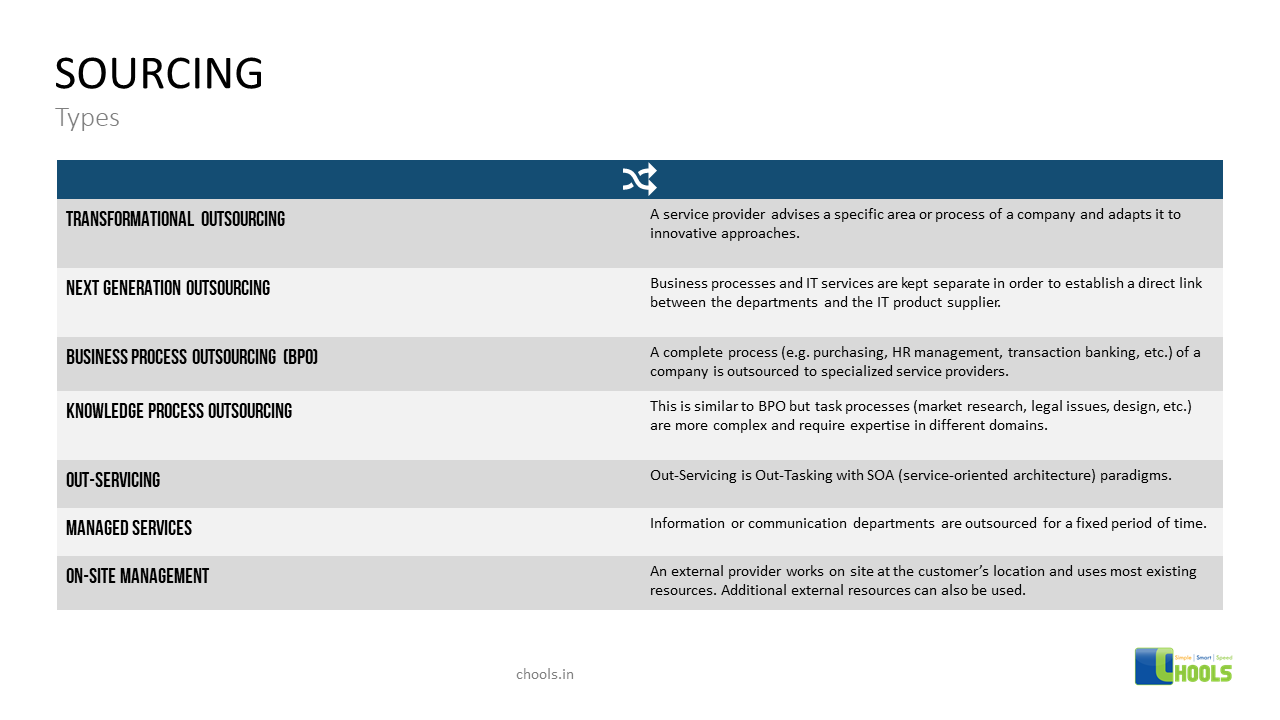
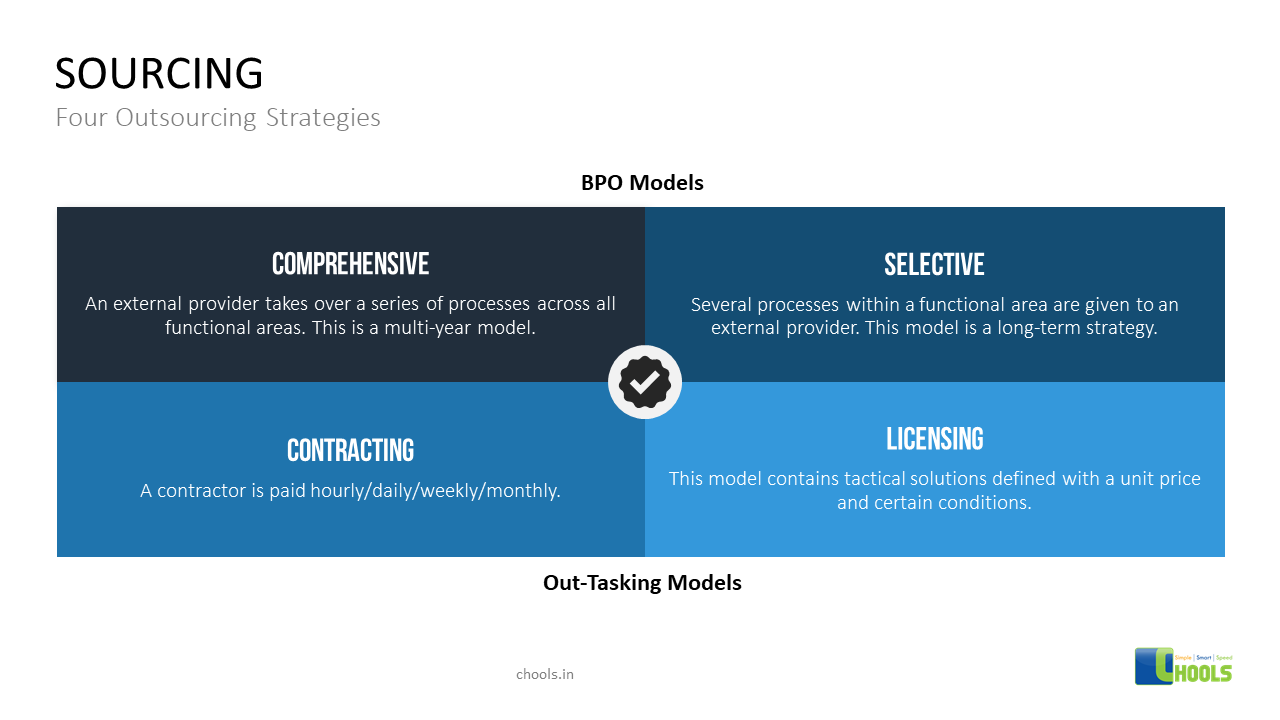
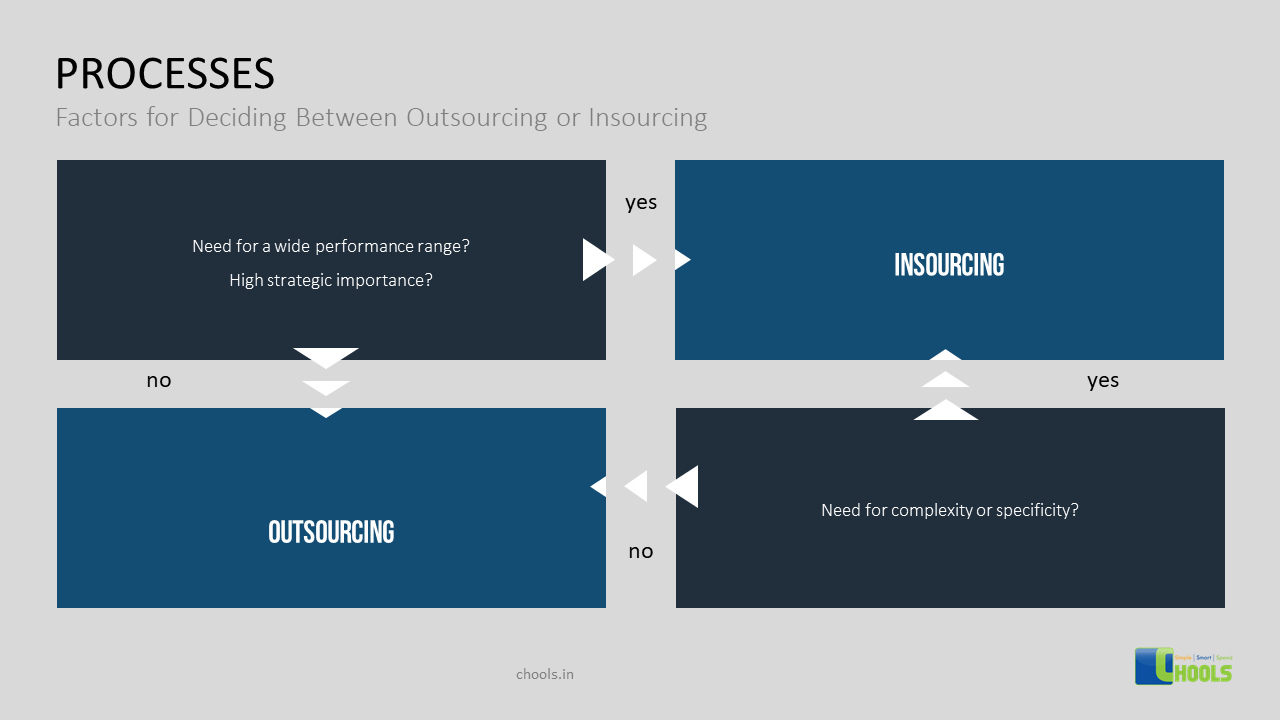
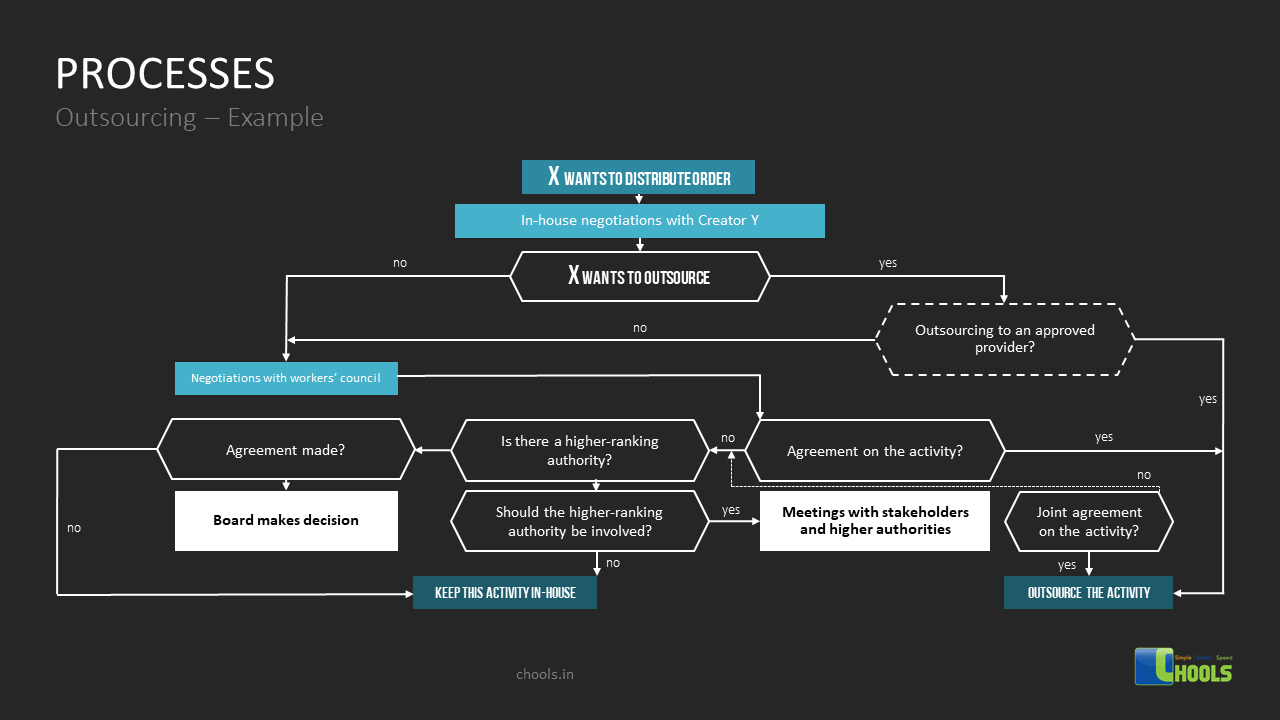
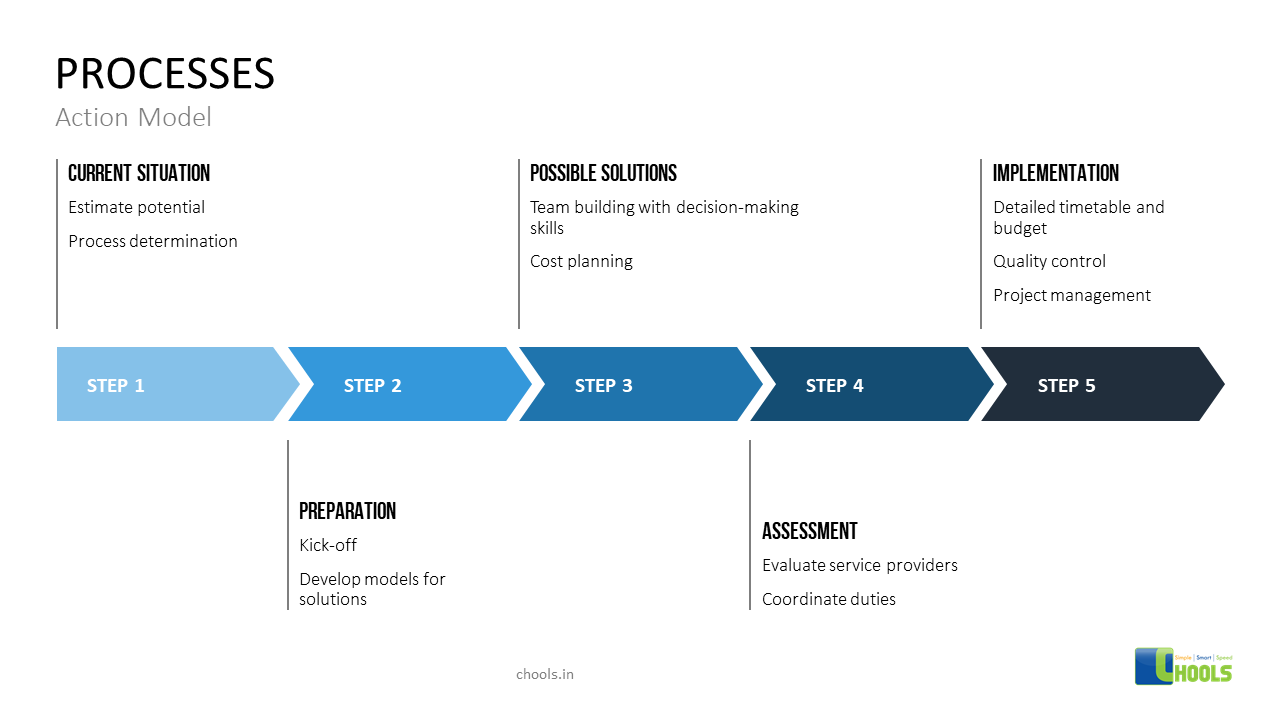
4. OUTSOURCING
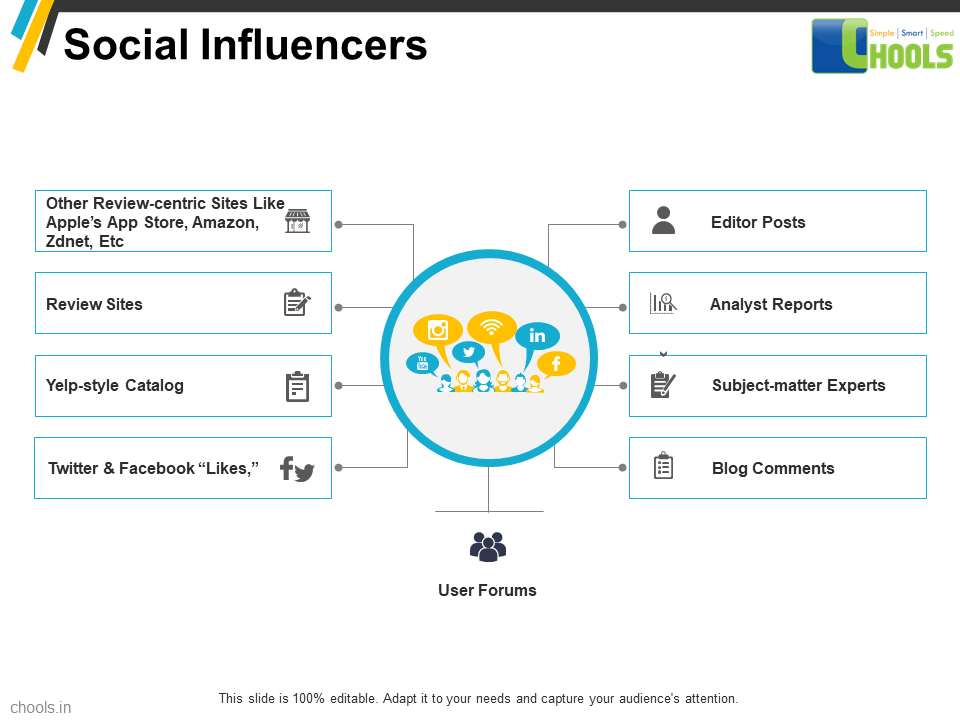
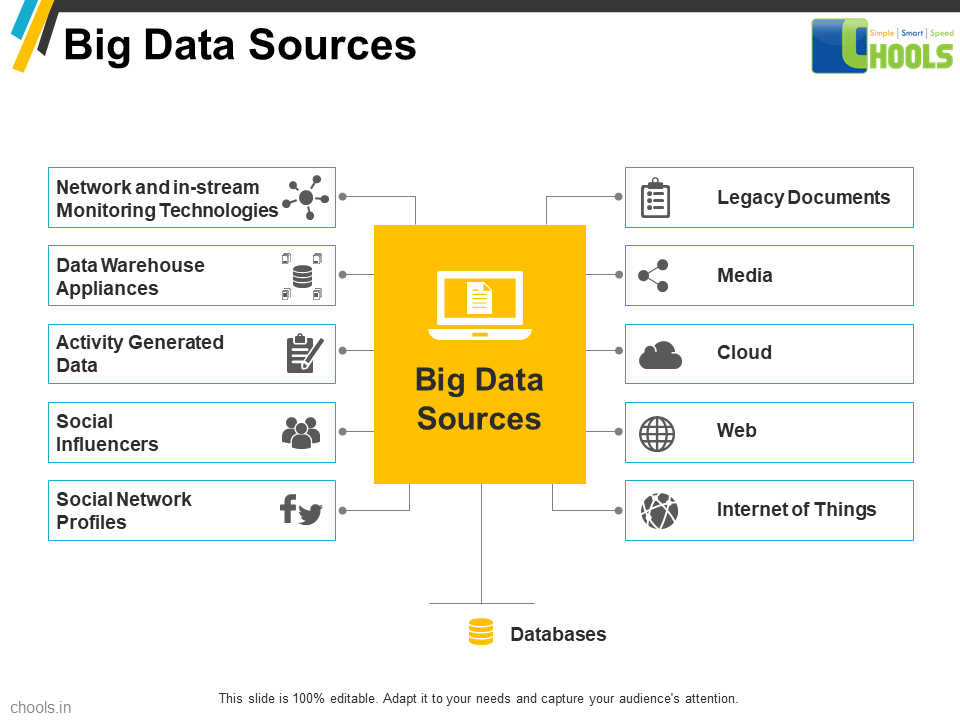
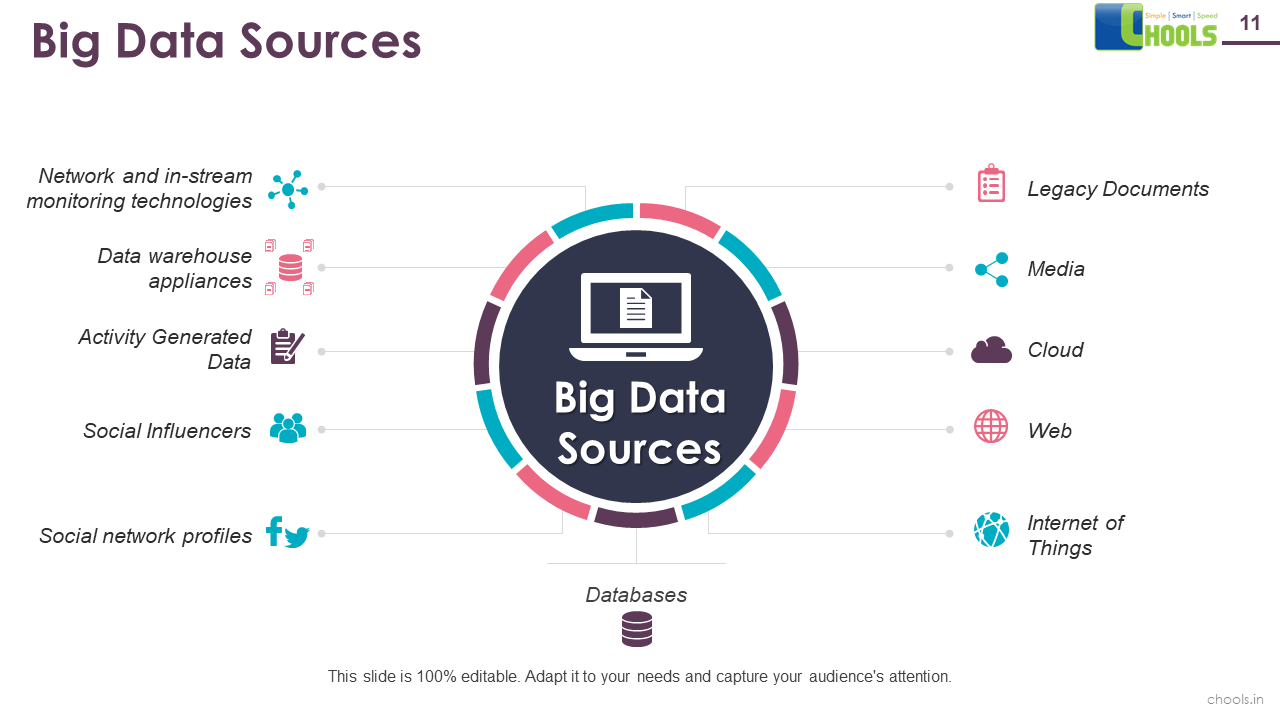
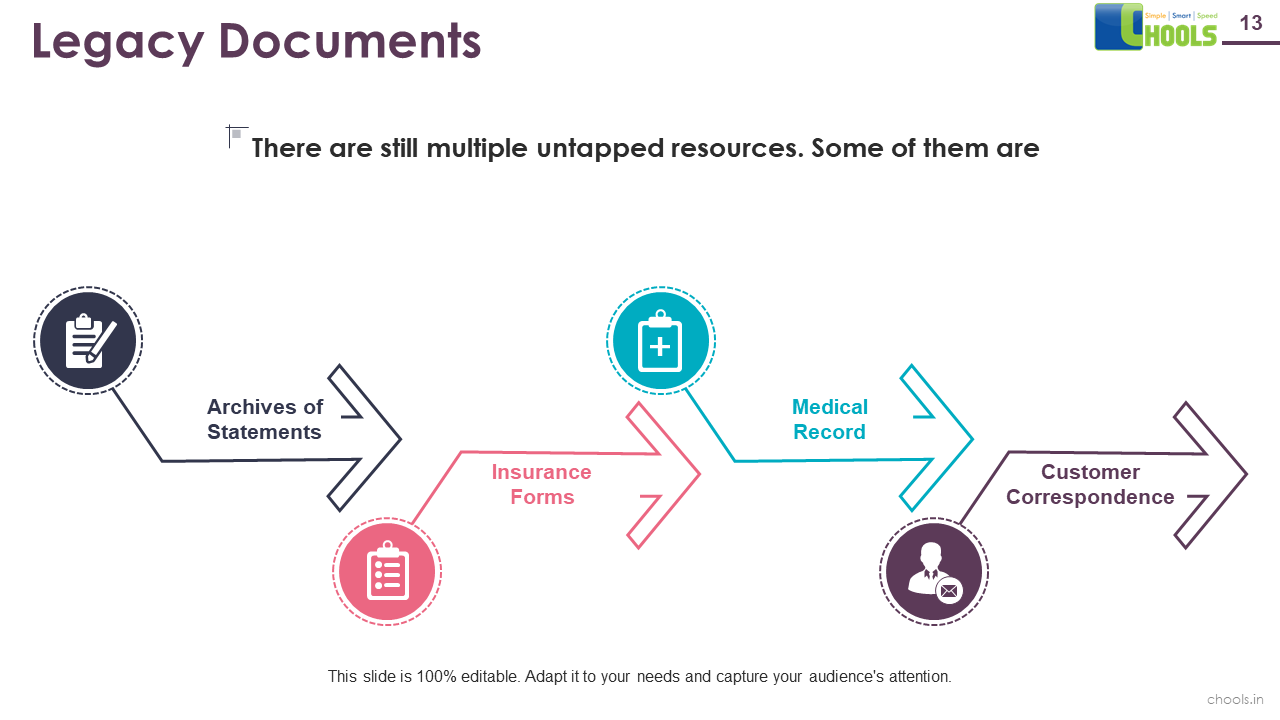
5. BIG DATA SOURCES